

400-9696-311 转1

400-9696-311 转2

400-9696-311 转3

400-9696-311 转4





ChiCTR2000033175
结束
/
/
/
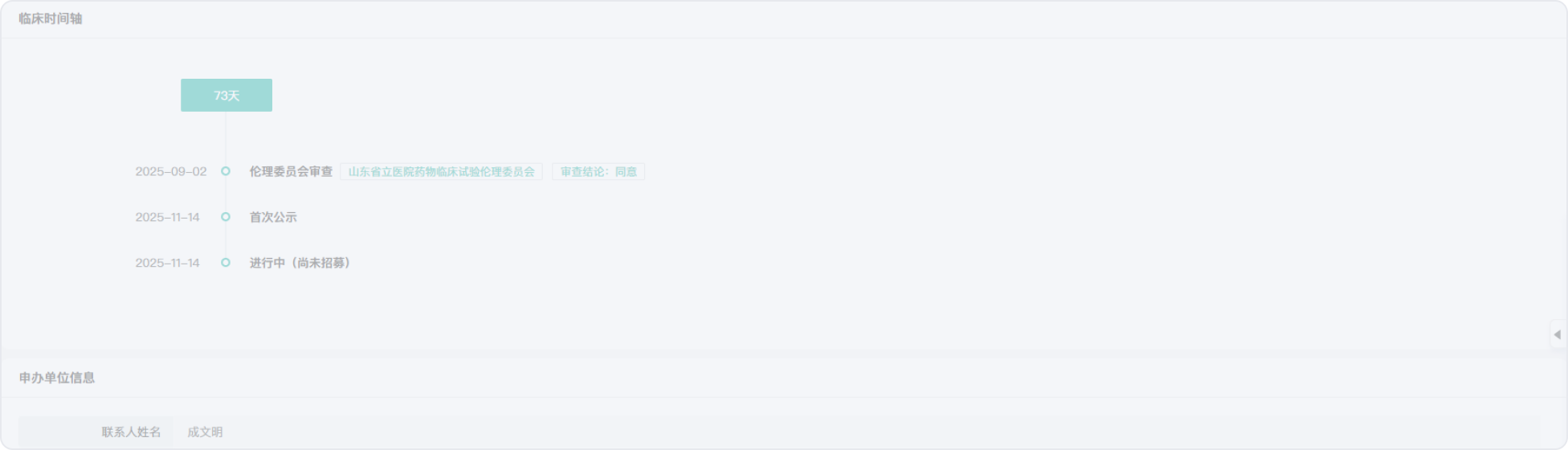
2020-05-23
/
/
Humeral shaft fractures
A multicentre randomized study comparing patient reported outcomes between surgical fixation versus conservative management in humeral shaft fractures in the elderly
A multicentre randomized study comparing patient reported outcomes between surgical fixation versus conservative management in humeral shaft fractures in the elderly
75500
Our aim is to directly compare these two methods. We want to find out whether arm function and quality of life in patients with this fracture is better with the more conservative cast and brace treatment or with surgery
随机平行对照
Ⅰ期+Ⅱ期
The study will use a parallel assignment model, with 1:1 allocation of patients into each treatment arm (operative or non-operative). Randomisation will be stratified by patient age (< 75 years old or ≥ 75 years old)
Not stated
Nil
/
100
/
2016-01-21
2020-05-29
/
1. Aged 60 years or older; 2. Unilateral displaced humeral shaft fracture; 3. Displacement was at least the amount of the thickness of the cortex or in transverse fractures diastasis of the half of the thickness of the cortex was required; 4. The fracture was lying in a zone delimited proximally by the superior border of the pectoralis major tendon attachment and distally by the line lying 5 cm from the upper border of the olecranon fossa as evaluated from the x-ray (see Figure 2 A in the main publication for illustration); 5. The fracture was less than 10 days old; 6. The patient was willing to accept both treatment options and willing to participate in all follow-up visits; 7. Patient spoke and read fluently either Finnish or Swedish (due to language used in data forms.;
请登录查看1. Bilateral fracture; 2. Fracture type where pectoralis major and deltoid muscle tendon insertions were in different fracture fragments causing typically significant fracture gap between the fragments (see Figure 2 B in the main publication for illustration); 3. Other concomitant trauma affecting the same upper extremity (fracture, tendon injury, significant soft tissue injury); 4. Other fracture, thoracic or abdominal injury requiring surgery; 5. Open fracture; 6. Pathologic fracture; 7. Polytraumatized patient; 8. Significant vascular injury warranting operative treatment; 9. Plexus injury; 10. History of trauma of the same upper extremity causing functional deficit; 11. Trauma or condition that warranted use of walking aid (crutches, wheelchair etc.); 12. Disease that significantly affected general condition of the patient; 13. Significantly impaired ability to co-operate for any reason (substance abuse, mental disorder, dementia); 14. Operative treatment unable to be performed within 14 days of trauma; 15. Unwilling to accept both treatment methods.;
请登录查看巴基斯坦拉合尔古尔基信托和教学医院
75500
求实药社2026-03-05
生物制品圈2026-03-05
医药观澜2026-03-05
医药观澜2026-03-05
河北省干细胞中心2026-03-05
生物制药小编2026-03-05
一度医药2026-03-05
炎明生物Pyrotech2026-03-05
药明康德2026-03-05
疑夕随笔2026-03-04